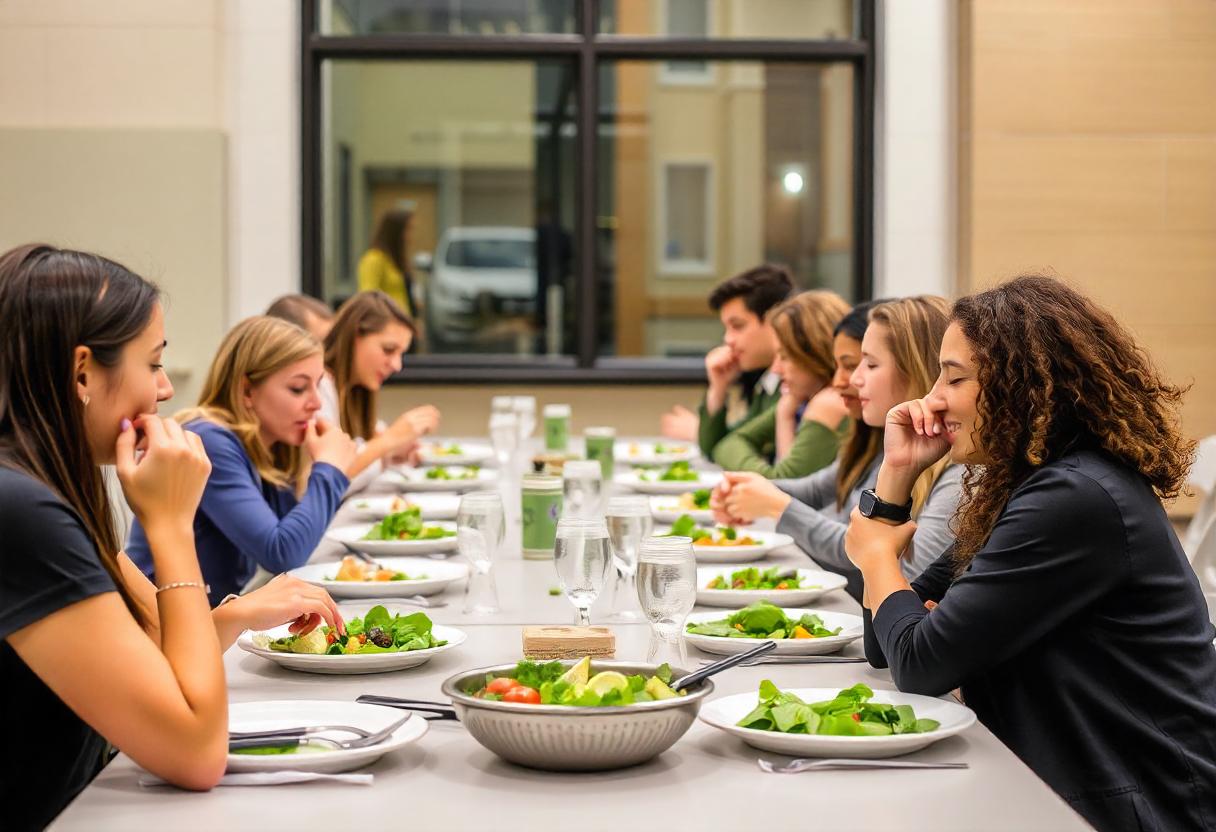
Benefits of Plant based food
Benefits of Plant based food
Benefits of Plant based food
Benefits of Plant based food
A plant-based diet is rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, all of which contribute to better heart health. Studies show that those who follow plant-based diets have a lower risk of heart disease and lower blood pressure levels.
A plant-based diet is rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, all of which contribute to better heart health. Studies show that those who follow plant-based diets have a lower risk of heart disease and lower blood pressure levels.
A plant-based diet is rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, all of which contribute to better heart health. Studies show that those who follow plant-based diets have a lower risk of heart disease and lower blood pressure levels.
A plant-based diet is rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, all of which contribute to better heart health. Studies show that those who follow plant-based diets have a lower risk of heart disease and lower blood pressure levels.
A plant-based diet is rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, all of which contribute to better heart health. Studies show that those who follow plant-based diets have a lower risk of heart disease and lower blood pressure levels.
Plant-based diets are often lower in calories and higher in fiber, which can help with weight management and reduce the risk of obesity. Fiber helps you feel full longer, reducing overall calorie intake.
Plant-based diets are often lower in calories and higher in fiber, which can help with weight management and reduce the risk of obesity. Fiber helps you feel full longer, reducing overall calorie intake.
Plant-based diets are often lower in calories and higher in fiber, which can help with weight management and reduce the risk of obesity. Fiber helps you feel full longer, reducing overall calorie intake.
Plant-based diets are often lower in calories and higher in fiber, which can help with weight management and reduce the risk of obesity. Fiber helps you feel full longer, reducing overall calorie intake.
Plant-based diets are often lower in calories and higher in fiber, which can help with weight management and reduce the risk of obesity. Fiber helps you feel full longer, reducing overall calorie intake.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:
Consuming more plant-based foods can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and high blood pressure. Phytochemicals in plants have been shown to have protective effects against these diseases.
Consuming more plant-based foods can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and high blood pressure. Phytochemicals in plants have been shown to have protective effects against these diseases.
Consuming more plant-based foods can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and high blood pressure. Phytochemicals in plants have been shown to have protective effects against these diseases.
Consuming more plant-based foods can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and high blood pressure. Phytochemicals in plants have been shown to have protective effects against these diseases.
Consuming more plant-based foods can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and high blood pressure. Phytochemicals in plants have been shown to have protective effects against these diseases.
The high fiber content in plant-based foods promotes healthy digestion by preventing constipation and supporting a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
The high fiber content in plant-based foods promotes healthy digestion by preventing constipation and supporting a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
The high fiber content in plant-based foods promotes healthy digestion by preventing constipation and supporting a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
The high fiber content in plant-based foods promotes healthy digestion by preventing constipation and supporting a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
The high fiber content in plant-based foods promotes healthy digestion by preventing constipation and supporting a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
Environmental Sustainability:
Environmental Sustainability:
Environmental Sustainability:
Plant-based diets have a lower environmental impact compared to diets high in animal products. They require fewer natural resources, such as water and land, and produce fewer greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Plant-based diets have a lower environmental impact compared to diets high in animal products. They require fewer natural resources, such as water and land, and produce fewer greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Plant-based diets have a lower environmental impact compared to diets high in animal products. They require fewer natural resources, such as water and land, and produce fewer greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Plant-based diets have a lower environmental impact compared to diets high in animal products. They require fewer natural resources, such as water and land, and produce fewer greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Plant-based diets have a lower environmental impact compared to diets high in animal products. They require fewer natural resources, such as water and land, and produce fewer greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Some studies suggest that plant-based diets may help improve mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. The antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals found in plants are beneficial for brain health.
Some studies suggest that plant-based diets may help improve mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. The antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals found in plants are beneficial for brain health.
Some studies suggest that plant-based diets may help improve mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. The antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals found in plants are beneficial for brain health.
Some studies suggest that plant-based diets may help improve mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. The antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals found in plants are beneficial for brain health.
Some studies suggest that plant-based diets may help improve mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. The antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals found in plants are beneficial for brain health.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds can improve skin health due to the high content of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help protect against skin aging and damage.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds can improve skin health due to the high content of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help protect against skin aging and damage.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds can improve skin health due to the high content of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help protect against skin aging and damage.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds can improve skin health due to the high content of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help protect against skin aging and damage.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds can improve skin health due to the high content of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help protect against skin aging and damage.
Enhanced Immune Function:
Enhanced Immune Function:
Enhanced Immune Function:
The vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in plant foods strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and illnesses more effectively.
The vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in plant foods strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and illnesses more effectively.
The vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in plant foods strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and illnesses more effectively.
The vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in plant foods strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and illnesses more effectively.
The vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in plant foods strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and illnesses more effectively.
A plant-based diet aligns with ethical concerns about animal welfare, as it reduces the demand for meat and animal products, which often come from industries with poor animal welfare practices.
A plant-based diet aligns with ethical concerns about animal welfare, as it reduces the demand for meat and animal products, which often come from industries with poor animal welfare practices.
A plant-based diet aligns with ethical concerns about animal welfare, as it reduces the demand for meat and animal products, which often come from industries with poor animal welfare practices.
A plant-based diet aligns with ethical concerns about animal welfare, as it reduces the demand for meat and animal products, which often come from industries with poor animal welfare practices.
A plant-based diet aligns with ethical concerns about animal welfare, as it reduces the demand for meat and animal products, which often come from industries with poor animal welfare practices.
Some people may experience fewer food allergies and intolerances on a plant-based diet, as it avoids common allergens found in animal products.
Some people may experience fewer food allergies and intolerances on a plant-based diet, as it avoids common allergens found in animal products.
Some people may experience fewer food allergies and intolerances on a plant-based diet, as it avoids common allergens found in animal products.
Some people may experience fewer food allergies and intolerances on a plant-based diet, as it avoids common allergens found in animal products.
Some people may experience fewer food allergies and intolerances on a plant-based diet, as it avoids common allergens found in animal products.
By adopting a plant-based diet, individuals can not only enhance their personal health but also contribute positively to the environment and support ethical food practices.
By adopting a plant-based diet, individuals can not only enhance their personal health but also contribute positively to the environment and support ethical food practices.
By adopting a plant-based diet, individuals can not only enhance their personal health but also contribute positively to the environment and support ethical food practices.
By adopting a plant-based diet, individuals can not only enhance their personal health but also contribute positively to the environment and support ethical food practices.
Food insecurity (Stats used from nj.gov)
Food insecurity
(Stats used from nj.gov)
Food insecurity
(Stats used from nj.gov)
Food insecurity
(Stats used from nj.gov)
In 2022, over 994,000 individuals experienced food insecurity in New Jersey. The food insecurity rate was 10.7% in New Jersey compared to 13.5% in the U.S.
The rate of food insecurity is higher among children (<18 years) with over 263,000 (13.2%) experiencing food insecurity in New Jersey in 2022.
Black (all ethnicities) (21.0%) and Latino (Hispanic) (20.0%) individuals experience food insecurity at higher rates than white (6.0%) individuals across New Jersey.
From 2018 to 2022, food insecurity in New Jersey has gotten worse, changing from 8.7% overall and 11.3% among children to 10.7% overall and 13.2% among children.
In 2022, over 994,000 individuals experienced food insecurity in New Jersey. The food insecurity rate was 10.7% in New Jersey compared to 13.5% in the U.S.
The rate of food insecurity is higher among children (<18 years) with over 263,000 (13.2%) experiencing food insecurity in New Jersey in 2022.
Black (all ethnicities) (21.0%) and Latino (Hispanic) (20.0%) individuals experience food insecurity at higher rates than white (6.0%) individuals across New Jersey.
From 2018 to 2022, food insecurity in New Jersey has gotten worse, changing from 8.7% overall and 11.3% among children to 10.7% overall and 13.2% among children.
In 2022, over 994,000 individuals experienced food insecurity in New Jersey. The food insecurity rate was 10.7% in New Jersey compared to 13.5% in the U.S.
The rate of food insecurity is higher among children (<18 years) with over 263,000 (13.2%) experiencing food insecurity in New Jersey in 2022.
Black (all ethnicities) (21.0%) and Latino (Hispanic) (20.0%) individuals experience food insecurity at higher rates than white (6.0%) individuals across New Jersey.
From 2018 to 2022, food insecurity in New Jersey has gotten worse, changing from 8.7% overall and 11.3% among children to 10.7% overall and 13.2% among children.
In 2022, over 994,000 individuals experienced food insecurity in New Jersey. The food insecurity rate was 10.7% in New Jersey compared to 13.5% in the U.S.
The rate of food insecurity is higher among children (<18 years) with over 263,000 (13.2%) experiencing food insecurity in New Jersey in 2022.
Black (all ethnicities) (21.0%) and Latino (Hispanic) (20.0%) individuals experience food insecurity at higher rates than white (6.0%) individuals across New Jersey.
From 2018 to 2022, food insecurity in New Jersey has gotten worse, changing from 8.7% overall and 11.3% among children to 10.7% overall and 13.2% among children.
In 2022, over 994,000 individuals experienced food insecurity in New Jersey. The food insecurity rate was 10.7% in New Jersey compared to 13.5% in the U.S.
The rate of food insecurity is higher among children (<18 years) with over 263,000 (13.2%) experiencing food insecurity in New Jersey in 2022.
Black (all ethnicities) (21.0%) and Latino (Hispanic) (20.0%) individuals experience food insecurity at higher rates than white (6.0%) individuals across New Jersey.
From 2018 to 2022, food insecurity in New Jersey has gotten worse, changing from 8.7% overall and 11.3% among children to 10.7% overall and 13.2% among children.